Unlocking the Secrets of GS Pay Progression
Ever wondered how your salary as a federal government employee on the General Schedule (GS) pay system progresses? It's not magic, but a structured system of within-grade increases, often referred to as step increases. Understanding the GS pay step increase schedule is crucial for planning your financial future and maximizing your earning potential. This article delves into the intricacies of this system, providing you with the knowledge you need to navigate your GS pay journey successfully.
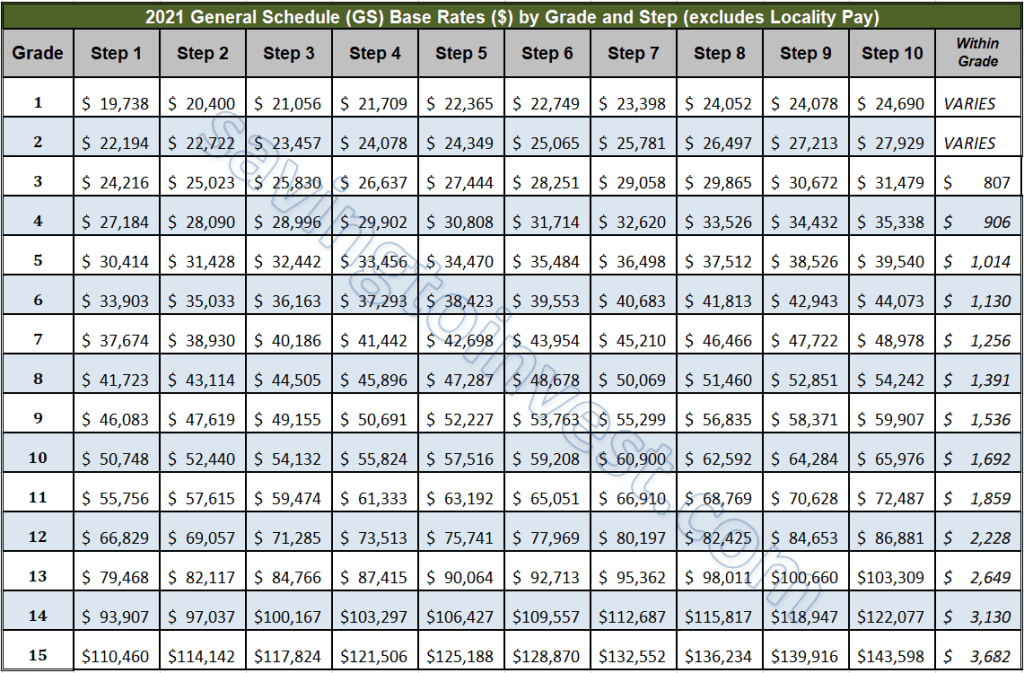
The GS pay system is the backbone of compensation for many federal employees. Within each GS grade, there are ten steps, each representing a specific salary level. Moving up these steps, typically through within-grade increases (WGIs), allows employees to earn more over time, rewarding experience and continued service. This system aims to motivate employees, recognize contributions, and foster a sense of stability and growth within the federal workforce.
The GS pay step increase schedule has its roots in the Classification Act of 1923, which laid the foundation for a standardized federal pay system. Over the years, it has evolved to meet the changing needs of the government and its employees. The significance of this schedule lies in its ability to provide a predictable and transparent path for salary growth, ensuring fair compensation and incentivizing career progression within the federal government.
A key issue related to the GS pay step increase schedule is ensuring that it remains competitive with the private sector. Factors like inflation, cost of living adjustments, and market conditions can impact the real value of GS salaries. Regular reviews and adjustments to the schedule are necessary to maintain its effectiveness in attracting and retaining top talent within the federal workforce.
A "within-grade increase" (WGI) is a periodic pay raise given to eligible federal employees within their current GS grade. These increases typically move an employee up one step within their grade. For instance, an employee at GS-9, Step 5, would move to GS-9, Step 6 after receiving a WGI. There are specific waiting periods between WGIs, typically one year at the beginning, and then two or three years for the following steps. Satisfactory performance is usually a requirement for receiving a WGI.
One benefit of the GS pay step increase schedule is predictability. Employees can generally anticipate when they'll receive a step increase, allowing for better financial planning. Another advantage is the inherent motivation for consistent performance. The prospect of regular pay increases encourages employees to meet or exceed performance expectations. Finally, the system promotes retention by offering a clear path for salary growth, reducing the likelihood of employees seeking better compensation elsewhere.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS Pay Step Increase Schedule
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Predictable salary growth | Potential for salary compression at higher grades |
| Motivates consistent performance | Limited flexibility in addressing individual performance differences |
| Promotes employee retention | Susceptible to budget constraints impacting adjustments |
Best Practices: 1. Understand your agency's specific WGI policies. 2. Regularly review your performance evaluations. 3. Communicate with your supervisor about your career goals. 4. Stay informed about changes to the GS pay schedule. 5. Utilize online resources and tools to calculate potential salary growth.
FAQs:
1. How often do I get a step increase? (Depends on your step and agency policy.)
2. What if my performance is not satisfactory? (You may not receive a WGI.)
3. Can I skip steps? (Sometimes, based on qualifications and recruitment needs.)
4. How are step increases calculated? (Based on predetermined percentages of the base salary for each grade.)
5. What about locality pay? (Locality pay is added on top of the base GS salary and step increase.)
6. Are step increases automatic? (Generally, after fulfilling the waiting period and satisfactory performance.)
7. What is a special rate table? (Used for specific occupations with higher pay needs.)
8. How can I find my current pay schedule? (OPM website or your agency's HR department.)
Tips and Tricks: Utilize the OPM website for up-to-date information. Keep a record of your performance evaluations. Understand the difference between within-grade increases and promotions. Factor in locality pay when calculating your total compensation.
In conclusion, the GS pay step increase schedule provides a structured framework for salary progression within the federal government. Understanding its nuances, including the waiting periods, performance requirements, and potential benefits, is crucial for navigating your career effectively. By leveraging the resources available, staying informed about updates, and actively managing your performance, you can maximize your earning potential and achieve your financial goals. This structured system empowers federal employees to plan for their future and focus on contributing their skills and expertise to public service, knowing their dedication and consistent performance are recognized and rewarded. Take the time to familiarize yourself with the intricacies of the GS pay step increase schedule and unlock its full potential for your career success. Your financial future deserves nothing less than your full attention and understanding of this important system.
Unlocking curb appeal sherwin williams exterior stain guide
Unraveling the enigma of elizabeth afton exploring the fnaf wiki universe
Unveiling farrow ball a wikipedia deep dive