Understanding Your Motorcycle's Starter Relay: A Comprehensive Guide

Ever wondered what that clicking sound is when you press your motorcycle's start button and nothing happens? It could be your starter relay. This small but crucial component plays a vital role in getting your engine roaring to life. Understanding its function can save you from roadside headaches and empower you to maintain your bike's starting system effectively.
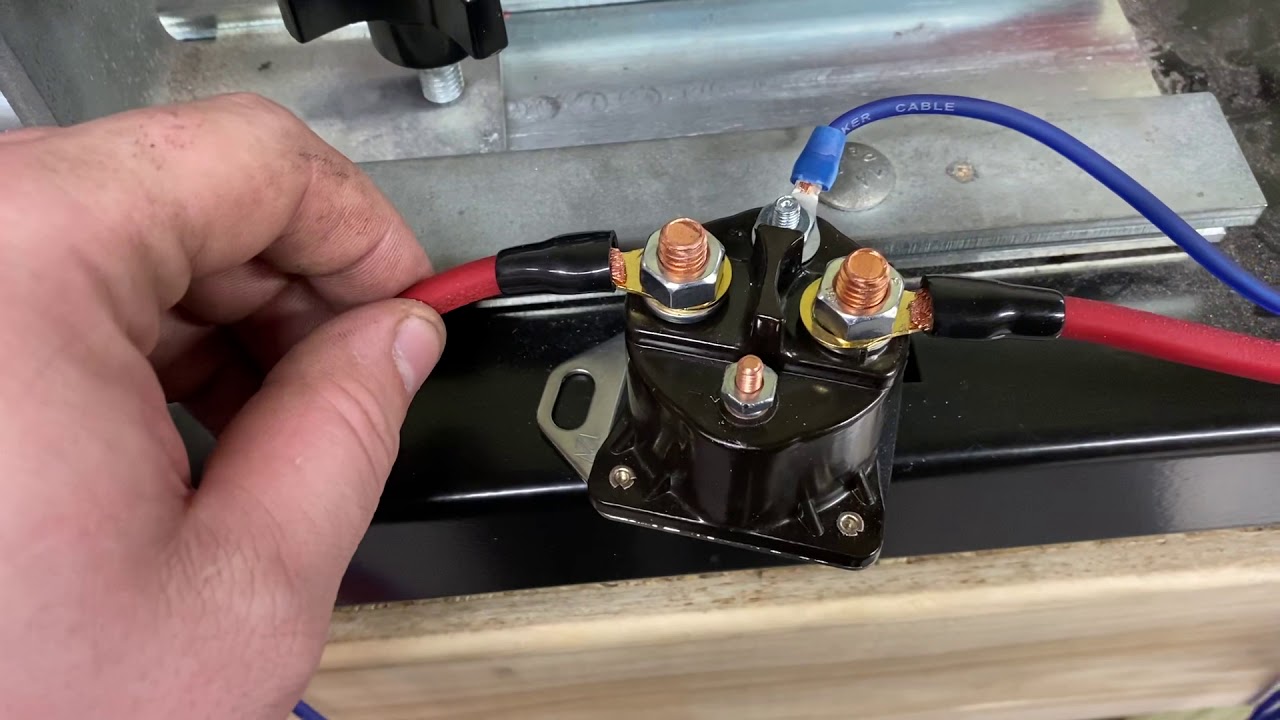
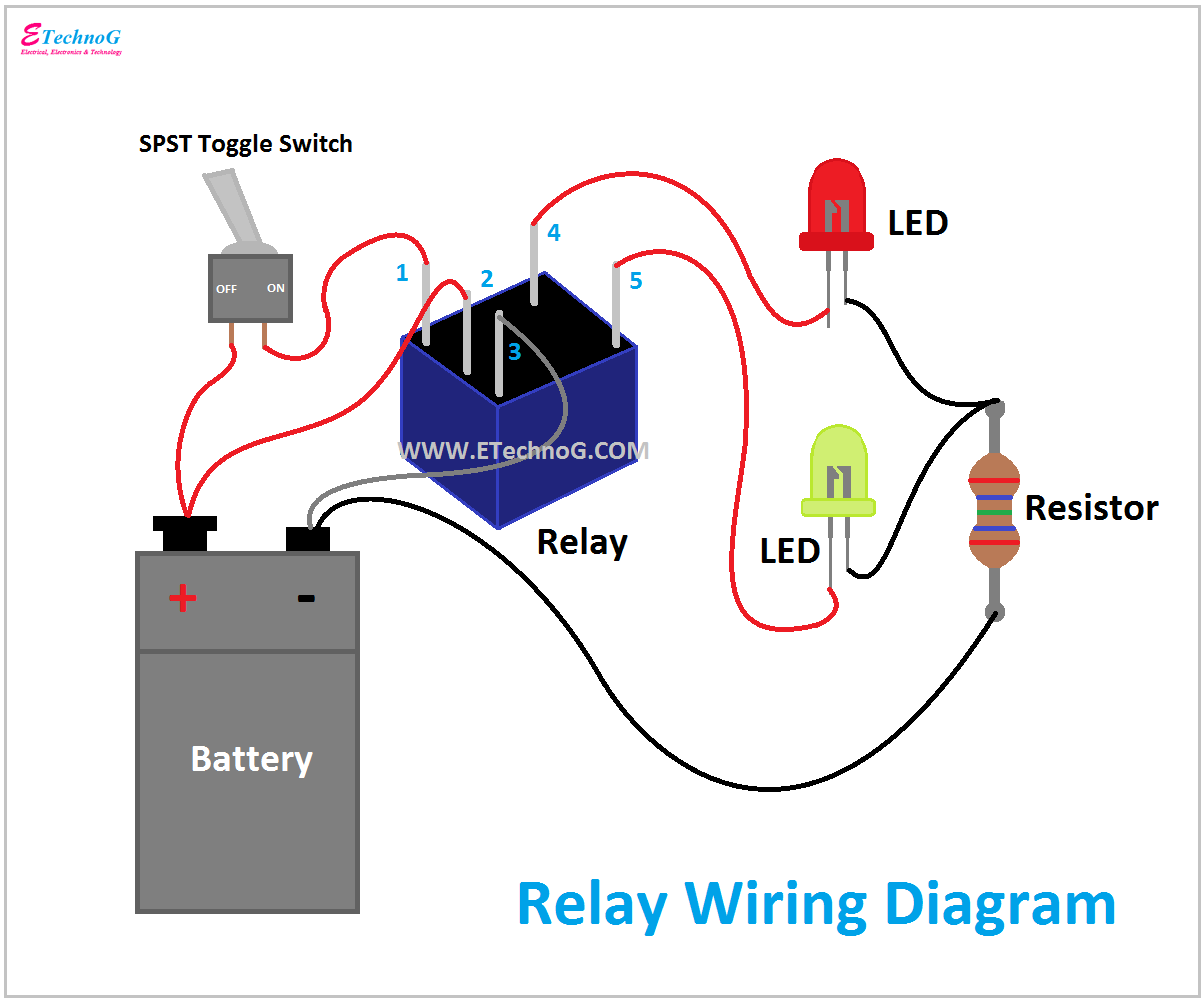
The starter relay acts as an electrical switch, connecting the battery's substantial current to the starter motor. Imagine trying to force a massive river through a small pipe – that's the kind of power surge the starter motor requires. The relay manages this flow, protecting the delicate circuitry of the start button and ensuring a reliable start-up every time.
The function of the starter relay is paramount. It safeguards your motorcycle's electrical system by preventing excessive current from damaging sensitive components. Without it, the start button would likely burn out quickly due to the high current required by the starter motor.
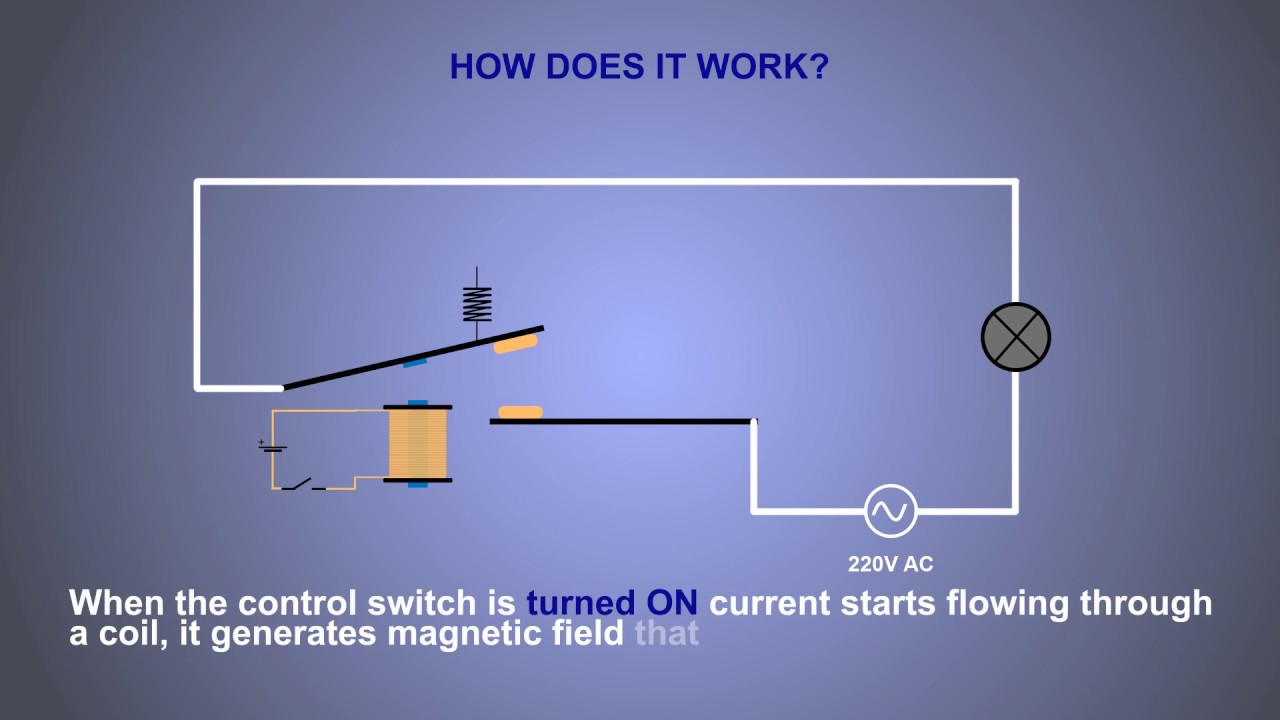
The starter relay is essentially a small electromagnet. When you press the start button, a small current energizes the relay's coil, creating a magnetic field. This magnetic field pulls a contact inside the relay, closing the circuit and allowing the high current from the battery to flow to the starter motor. Once the engine starts, the starter button is released, the relay de-energizes, and the circuit opens.
Malfunctioning starter relays are a common motorcycle issue. Symptoms of a faulty relay include a clicking sound from the relay itself, the engine not cranking at all, or intermittent starting problems. Luckily, testing and replacing a starter relay is usually a straightforward and inexpensive fix.
Historically, early motorcycles relied on kick-starting, a physically demanding process. The introduction of electric starters significantly improved rider convenience. The starter relay evolved alongside these advancements, becoming an essential part of the modern motorcycle's electrical system.
A key issue related to motorcycle starter relay function is corrosion. Exposed contacts can corrode over time, impeding the flow of electricity and hindering the relay's operation. Regularly cleaning the relay's terminals can prevent this problem.
One of the key benefits of a starter relay is its ability to protect the start button on your motorcycle's handlebar control. The high amperage required to crank the engine would quickly damage a standard switch, therefore, the relay acts as an intermediary, using a small current to control a much larger one.
Another benefit is its ability to handle the high current surge required by the starter motor. The starter motor draws a significant amount of power, and the relay ensures that this power is delivered efficiently and safely.
Finally, the relay simplifies the wiring of the starting circuit. Instead of running thick, heavy-gauge wires all the way to the start button, the relay allows for the use of thinner wires for the control circuit, making installation and maintenance easier.
If you suspect a faulty starter relay, you can test it using a multimeter. Connect the meter to the relay's terminals and check for continuity. A functioning relay will show continuity when energized.
Replacing a motorcycle starter relay is generally a simple process. Locate the relay (usually near the battery), disconnect the wires, and install the new relay. Ensure the new relay has the same specifications as the old one. This can often be done with basic hand tools and minimal mechanical experience.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Starter Relay
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Protects the start switch | Subject to corrosion |
| Handles high current | Can fail mechanically or electrically |
| Simplifies wiring | Requires periodic inspection |
Best practices for maintaining your starter relay include keeping the terminals clean and free from corrosion, ensuring the battery connections are secure, and periodically inspecting the relay for signs of damage. One example of a relay issue is a clicking sound, usually near the battery compartment, when trying to start the motorcycle but the engine doesn't turn over.
FAQs
Q: What does a motorcycle starter relay do? A: It acts as a switch, allowing high current from the battery to flow to the starter motor.
Q: How do I test a starter relay? A: Use a multimeter to check for continuity.
Q: What are the signs of a bad starter relay? A: Clicking sounds, engine not cranking, intermittent starting problems.
Q: Can I bypass a starter relay? A: It is possible but not recommended due to safety concerns.
Q: Where is the starter relay located? A: Usually near the battery.
Q: How much does a starter relay cost? A: Relatively inexpensive, typically under $20.
Q: How long does a starter relay last? A: Several years, depending on usage and environmental conditions.
Q: Can I replace a starter relay myself? A: Yes, it's a relatively easy DIY task.
Tips and tricks for dealing with starter relay issues include carrying a spare relay, cleaning the terminals regularly, and checking the battery connections. A simple cleaning can often resolve intermittent starting problems.
In conclusion, the starter relay is a critical component of your motorcycle's starting system. Its ability to manage the high current flow to the starter motor ensures a reliable start and protects your bike's electrical system. Understanding how it works, how to troubleshoot issues, and performing regular maintenance can keep your motorcycle running smoothly for years to come. Investing a little time in learning about this small but vital part can save you from frustrating roadside breakdowns and expensive repairs. Ensure you prioritize regular checks and maintenance of your starter relay as part of your overall motorcycle care routine. This proactive approach will contribute to a smoother and more reliable riding experience.
Discover the magic of diving in split croatia
Navigating the uncharted waters of mafs chapter 2607
Unlocking shel silversteins giving tree poems lessons and legacy