Understanding Federal Pay Grades and Steps
Ever wondered how salaries are determined for federal government employees? The system, known as the General Schedule (GS), can seem complex at first glance. This comprehensive guide will break down the intricacies of federal government pay grades and steps, providing a clear understanding of how this structured system impacts federal employee compensation and career progression. We'll explore the history and significance of the GS system, discuss its benefits and challenges, and offer practical tips for navigating this critical aspect of federal employment.
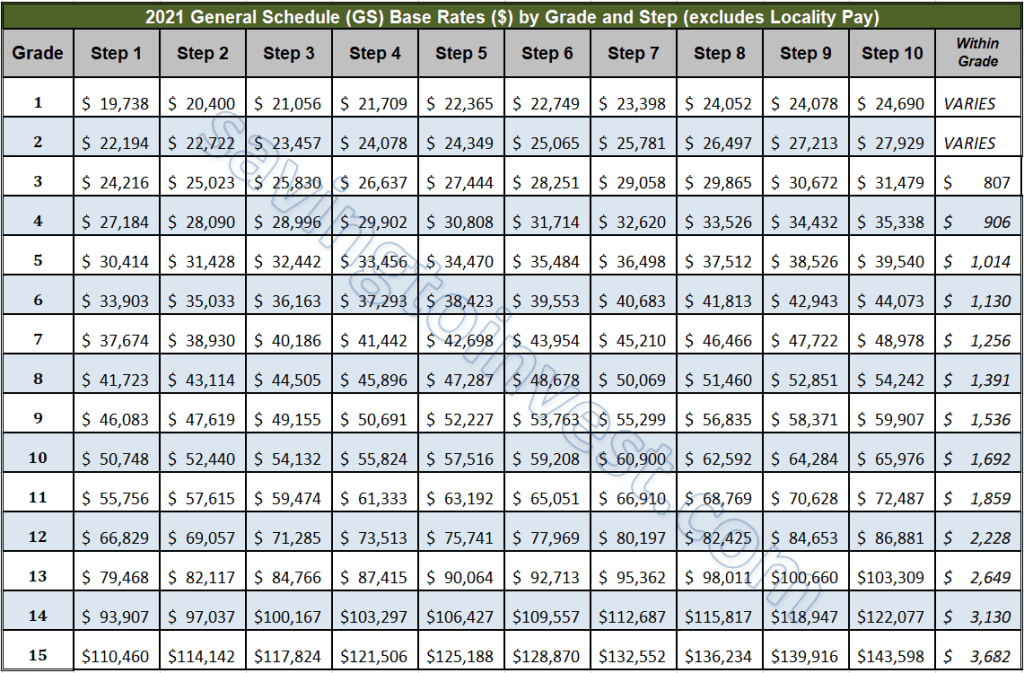
The federal pay grade structure is a tiered system, ranging from GS-1 to GS-15, with each grade representing a different level of responsibility and expertise. Within each grade are ten steps, reflecting longevity and performance. This stepwise progression provides a clear path for salary increases within a given grade. Understanding these fundamental components is essential for anyone considering or currently pursuing a career in federal service.
The GS system, established in 1949, aimed to create a standardized and fair compensation system across the various federal agencies. Before its implementation, pay practices varied widely, creating inconsistencies and potential inequities. The GS system brought order and transparency to federal compensation, ensuring equal pay for equal work, regardless of the specific agency. This standardization was a landmark achievement in government personnel management.
The importance of understanding federal pay grades and steps extends beyond simply knowing your salary. It directly impacts career advancement opportunities, as promotions often involve moving to a higher pay grade. Furthermore, many federal benefits, such as retirement calculations, are tied to an employee's highest achieved pay grade. Therefore, grasping the nuances of the GS system is crucial for long-term career planning and financial security within the federal government.
One common issue surrounding federal pay grade classifications is the potential for misclassification. Accurately aligning a position's duties and responsibilities with the appropriate pay grade is crucial for both the employee and the government. Misclassification can lead to underpayment or overpayment, requiring adjustments and potentially causing dissatisfaction. Proper position classification is a vital aspect of maintaining a fair and equitable compensation system.
A federal pay grade level signifies a specific range of salaries. A step, within a grade, indicates a particular salary level within that range. For example, a GS-7, Step 5 employee earns more than a GS-7, Step 1 employee, but less than a GS-9 employee at any step. This structured progression incentivizes performance and rewards experience.
Benefits of the structured pay system include: 1) Transparency and Predictability - Employees can easily understand the salary potential within their chosen career path. 2) Fairness and Equity - Standardized grades and steps promote consistent compensation across different agencies. 3) Motivation and Career Progression - The step increases and potential for grade promotions incentivize performance and career development.
Advantages and Disadvantages of the GS System
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Transparency | Rigidity |
| Fairness | Potential for Bureaucracy |
| Predictability | Difficulty in Addressing Unique Skill Sets |
Best Practices: 1) Research your target position’s typical pay grade. 2) Understand the criteria for step increases. 3) Negotiate your starting step during the hiring process. 4) Document your accomplishments to support promotion requests. 5) Seek guidance from your agency’s human resources department.
Frequently Asked Questions: 1) How are federal pay grades determined? 2) How do I advance to a higher step? 3) What is a locality pay adjustment? 4) How do promotions affect my pay grade? 5) Can I negotiate my starting pay grade? 6) How does the GS system impact retirement benefits? 7) Where can I find more information on federal pay grades? 8) What are some common misconceptions about the GS system? (General answers should be provided to each question.)
Tips: Utilize online resources like the OPM website. Consult with colleagues or mentors experienced in the federal system. Stay updated on any changes to the GS pay scales.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of federal pay grades and steps is crucial for anyone considering or currently employed in the federal government. The GS system, while complex, provides a structured and transparent framework for compensation and career advancement. By grasping the fundamental concepts of grades, steps, locality pay adjustments, and promotion criteria, federal employees can effectively navigate their career paths and maximize their earning potential. Learning about the GS system isn't just about understanding your paycheck; it's about understanding your career trajectory within the federal government. Take the time to research, ask questions, and plan strategically to fully leverage the benefits of this structured pay system. This knowledge empowers federal employees to make informed decisions about their careers and achieve their long-term financial goals.
Decoding medicare part a amp b drug coverage
Conquering the road your guide to hgv wheel nut torque wrenches
Unlocking elegant lettering your guide to calligraphy pdf books