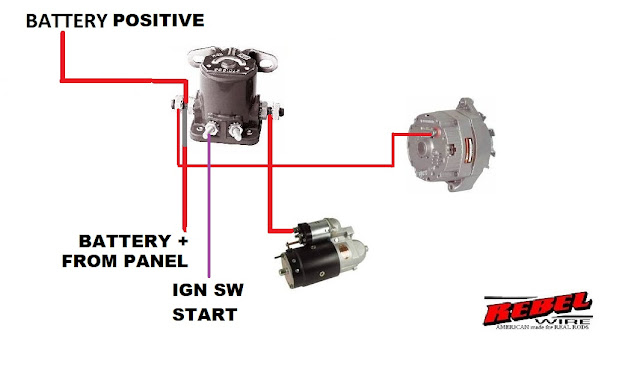
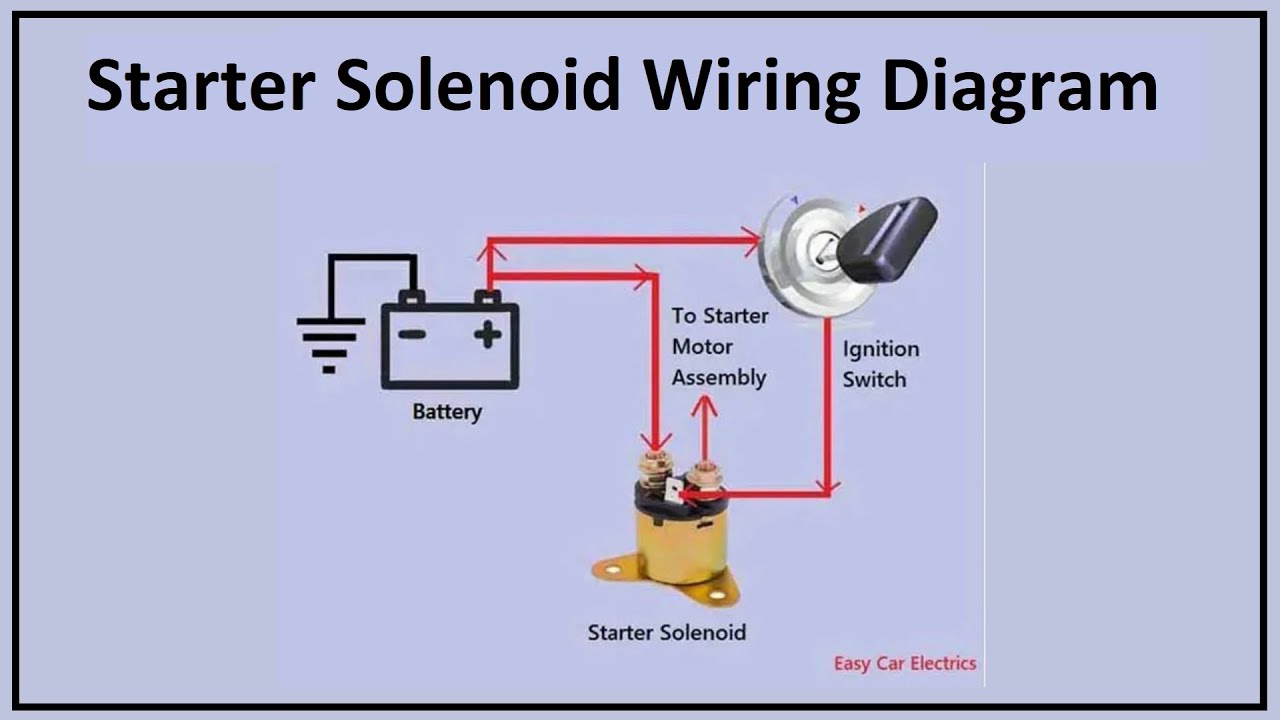
Decoding the Ford Starter Solenoid: Wiring Insights

The quiet hum of anticipation, the turn of the key, and then…nothing. A dead engine can be a frustrating experience, and often the culprit lies within the starter system, particularly the solenoid. Understanding the intricacies of your Ford starter solenoid wiring is crucial for diagnosing and resolving starting issues. This guide delves into the essential aspects of Ford starter solenoid wiring instructions, providing a foundation for both novice mechanics and seasoned DIY enthusiasts.
Navigating the network of wires under the hood can feel daunting. But, just like a well-tailored suit, each connection in the starter circuit has a specific purpose and place. The Ford starter solenoid acts as an intermediary between the ignition switch and the starter motor, delivering the high current necessary to crank the engine. Getting the wiring correct is fundamental for a reliable starting system.
The starter solenoid's history is intertwined with the evolution of the automobile. Early vehicles relied on hand cranks, a laborious and sometimes dangerous method. The introduction of the electric starter revolutionized the driving experience, and the solenoid became an integral part of this system, ensuring a controlled and powerful burst of energy to the starter motor. For Ford vehicles, the starter solenoid has been a consistent component across generations, though the specifics of its wiring have evolved.
The importance of correct Ford starter solenoid wiring cannot be overstated. A faulty connection or improper wiring can lead to a range of problems, from a simple click to no start at all, a drained battery, or even damage to other electrical components. Understanding the wiring diagram specific to your Ford model is crucial. These diagrams, often found in repair manuals or online resources, provide a visual roadmap of the starter circuit.
Common issues related to Ford starter solenoid wiring include corroded connections, loose wires, a faulty solenoid itself, or a problem with the ignition switch. Troubleshooting these issues often involves checking the voltage at various points in the circuit using a multimeter. This can help identify the source of the problem and guide the repair process. Let’s delve into understanding the core principles.
The solenoid essentially acts as a heavy-duty relay. When you turn the ignition key to the "start" position, a small current is sent to the solenoid, energizing its internal coil. This creates a magnetic field that pulls a plunger, closing a set of high-current contacts. These contacts then allow a large current to flow from the battery to the starter motor, cranking the engine.
Benefits of understanding Ford starter solenoid wiring instructions include: 1) Enabling you to troubleshoot starting issues effectively. 2) Saving money on potentially unnecessary repairs. 3) Empowering you to perform basic maintenance on your Ford vehicle.
If you suspect a solenoid issue, follow these steps: 1) Consult your vehicle's wiring diagram. 2) Check for loose or corroded connections. 3) Test the solenoid using a multimeter to ensure it's receiving power and engaging the starter motor. 4) If necessary, replace the solenoid with a compatible part.
Advantages and Disadvantages of DIY Ford Starter Solenoid Wiring
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Cost savings | Risk of incorrect wiring |
| Increased knowledge of your vehicle | Potential for damage to electrical components |
| Sense of accomplishment | Time investment |
Best Practices: 1) Always disconnect the battery before working on the starter circuit. 2) Use the correct gauge wiring for your vehicle. 3) Secure all connections tightly. 4) Double-check your work using a wiring diagram. 5) If unsure, consult a qualified mechanic.
FAQ: 1) What causes a clicking solenoid? A: Low battery voltage, faulty solenoid, or bad connections. 2) Can I bypass the solenoid to start the car? A: Yes, temporarily, but it’s not a long-term solution. 3) How do I test a solenoid with a multimeter? A: Check for voltage at the solenoid terminals. 4) Where is the solenoid located? A: Typically mounted on the starter motor. 5) What are the symptoms of a bad solenoid? A: Clicking sound, no crank, intermittent starting issues. 6) How much does a new solenoid cost? A: Varies depending on the vehicle model. 7) Can a bad solenoid drain the battery? A: A sticking solenoid can. 8) What tools do I need to replace a solenoid? A: Basic hand tools and a multimeter.
Tips: Use dielectric grease on connections to prevent corrosion. Keep wiring away from heat sources. Regularly inspect the starter circuit for signs of wear.
Mastering the nuances of your Ford starter solenoid wiring is like adding a crucial stitch to the fabric of your automotive knowledge. Understanding its function, troubleshooting common issues, and adhering to best practices empower you to maintain a reliable starting system, ensuring your Ford is always ready to hit the road. This detailed guide provides the foundation you need to confidently address starter problems, saving you time, money, and frustration. By understanding the intricacies of the starter circuit, you’re taking control of your vehicle’s health and ensuring its longevity. Remember, a well-maintained vehicle is a reflection of its owner's care and attention, much like a well-chosen ensemble speaks volumes about personal style.
Locating mr mime in pokemon sword your guide
Dead battery find a car battery jump starter portable near you
Mariano diaz wiki controversies understanding the online narrative