Decoding Heat Pump Heating: An Efficient Warmth

Imagine a crisp winter morning. The air bites with a frosty chill, yet inside, a gentle warmth envelopes you. This comfort could be thanks to a heat pump, a device increasingly lauded for its energy efficiency and environmentally friendly operation. But how does a heat pump actually generate heat, especially when the outside air is freezing? This is the question we'll unpack, delving into the intricacies of this increasingly popular heating solution.
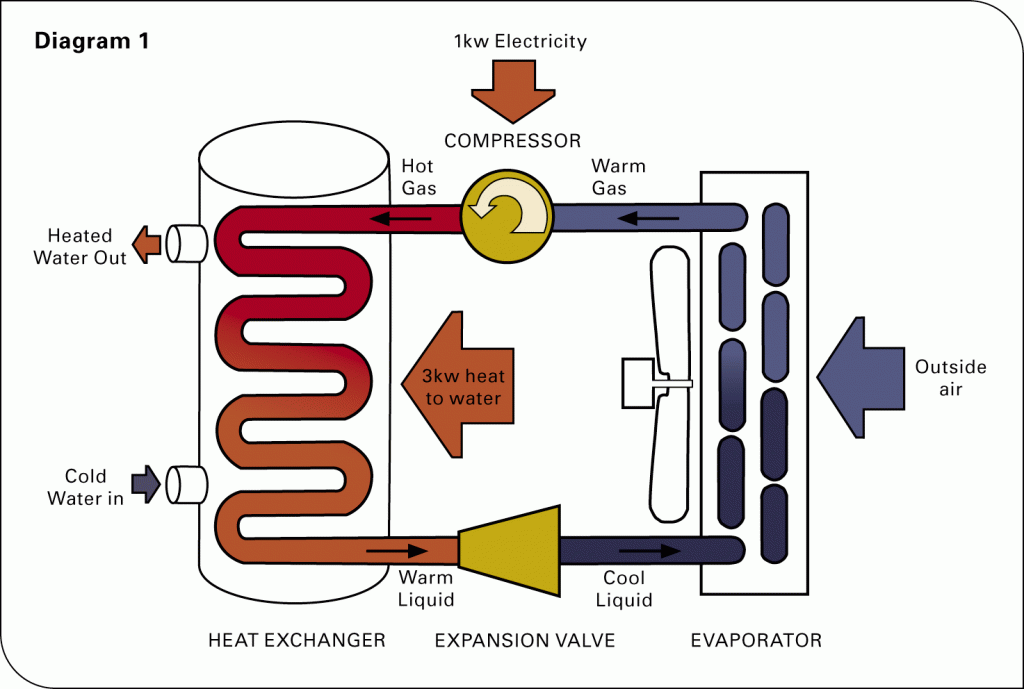
Rather than generating heat directly like a furnace, a heat pump cleverly moves heat from one place to another. Think of it as a refrigerator in reverse. In the summer, your refrigerator extracts heat from the inside and expels it to the outside, making the inside cool. A heat pump, in heating mode, absorbs heat from the outside air (even cold air contains some heat energy) and transfers it indoors.
The magic lies in the refrigerant, a special fluid within the heat pump system. This refrigerant cycles through a loop, changing its state from liquid to gas and back again. As it absorbs heat from the outside, it evaporates into a gas. Then, through compression, its temperature is raised significantly. This hot gas then passes through an indoor coil, releasing the stored heat into your home’s air distribution system. This continuous cycle effectively warms your home, drawing on the ambient outdoor air as its heat source.
The origins of heat pump technology can be traced back to the mid-19th century, with the development of refrigeration cycles. Over time, this technology evolved, leading to the creation of the modern heat pump. The growing awareness of energy conservation and environmental sustainability has propelled heat pumps to the forefront of home heating solutions.
One key issue related to heat pump functionality is their performance in extremely cold climates. While they operate effectively in moderate winters, their efficiency can decrease as the temperature drops significantly. This is because extracting heat from frigid air becomes more challenging. However, advancements in heat pump technology, such as cold-climate heat pumps, are addressing this limitation, enabling efficient operation even in sub-zero temperatures.
Heat pump heating offers several compelling advantages. Firstly, it's incredibly energy-efficient, often using significantly less energy than traditional heating systems. This translates into lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. Secondly, heat pumps offer both heating and cooling functionality, eliminating the need for separate systems. Thirdly, they are generally safer than combustion-based heating systems, as they don't involve burning fuel.
Considering a heat pump? Assess your climate, home size, and insulation. Consult with HVAC professionals to determine the right size and type of heat pump for your needs. Ensure proper installation for optimal performance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Heat Pump Heating
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Energy-efficient | Lower efficiency in extreme cold |
| Heating and cooling capability | Higher upfront cost |
| Environmentally friendly | May require supplemental heating in very cold climates |
Best Practices: 1. Regular maintenance. 2. Proper sizing. 3. Adequate insulation. 4. Thermostat optimization. 5. Professional installation.
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. How does a heat pump work in cold weather? - It extracts heat from the outside air, even when it's cold.
2. Are heat pumps expensive? - The initial cost is higher, but long-term savings offset this.
3. What is the lifespan of a heat pump? - Typically 15-20 years with proper maintenance.
4. Can a heat pump heat my entire home? - Yes, if properly sized.
5. Do heat pumps require ductwork? - Most do, but ductless options are available.
6. Are heat pumps noisy? - Modern heat pumps are relatively quiet.
7. What is the difference between a heat pump and an air conditioner? - A heat pump can both heat and cool.
8. What maintenance is required for a heat pump? - Regular filter changes and professional inspections.
Tips and tricks: Regularly clean or replace filters, schedule annual maintenance checks, and optimize thermostat settings for efficiency.
In conclusion, heat pump heating represents a significant advancement in home comfort and energy efficiency. By understanding how these systems function—extracting and transferring heat rather than generating it—we can appreciate their ingenuity. The benefits are clear: lower energy bills, reduced environmental impact, and year-round climate control. While initial costs might be higher than traditional systems, the long-term savings and environmental benefits make heat pumps a compelling choice for modern homes. Embracing this technology is not just a smart financial move but also a step towards a more sustainable future. If you're seeking an efficient and environmentally conscious heating solution, explore the possibilities of heat pump technology. Consult with HVAC professionals to determine the best system for your home and begin enjoying the comfort and savings it offers. Taking the time to understand and implement heat pump technology can significantly enhance your home's comfort and contribute to a greener future.
Hajj badal registration with tabung haji a comprehensive guide
Jl audio tower speakers unleash the sonic beast
Master skip bo your youtube guide to winning